(Report Producer/Author: Dongfang Securities, Liu Yang)
1. Favorable timing and location: The combination of the "dual carbon" policy and the temporary peak of domestic scrap aluminum recycling opens up space for the development of recycled aluminum
1.1 The "ceiling" of electrolytic aluminum production capacity is approaching, and policies continue to be favorable for recycled aluminum
The domestic electrolytic aluminum production capacity is expected to approach the "ceiling" in 2022, and the new supply may rely on recycled aluminum. As of the end of 2020, China's electrolytic aluminum production capacity has reached 42.56 million tons. According to data from Baichuan Yingfu, China may add 2.005 million tons of electrolytic aluminum production capacity in 2021, and by the end of 2021, China's electrolytic aluminum production capacity will reach 44.56 million tons. Domestic electrolytic aluminum production capacity is approaching its "ceiling", and new supply may rely on recycled aluminum.
Recycled aluminum has obvious advantages in energy conservation and emission reduction. The energy consumption of producing 1 ton of recycled aluminum is only 3% to 5% of that of electrolytic aluminum, which can reduce 0.8 tons of carbon dioxide emissions, save more than 10 tons of water, and reduce the treatment of solid waste, waste liquid, and waste residue, with obvious energy-saving and emission reduction advantages.
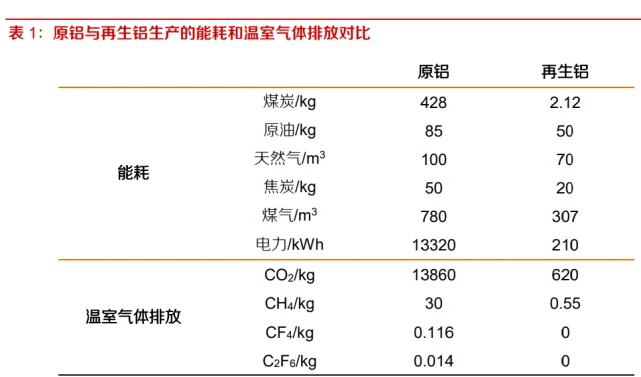
The policy continues to be favorable for recycled aluminum. The recycled aluminum industry uses various waste aluminum materials to produce aluminum alloy ingots, which significantly reduces thermal energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions compared to the industrial routes of bauxite, alumina, electrolytic aluminum, and aluminum alloys. The recycled aluminum industry has significant social benefits in terms of resource conservation, energy conservation, emission reduction, and environmental protection. The recycled aluminum industry belongs to the encouraged industries specified in the "Guiding Catalogue for Industrial Structure Adjustment" and has received support from national industrial policies. In the future, with the maintenance and utilization of scrap aluminum and the improvement of the recycling system, the industry space for recycled aluminum will continue to open up.
1.2 Domestic aluminum products are gradually reaching the end of their service life, and the supply of scrap aluminum is expected to increase
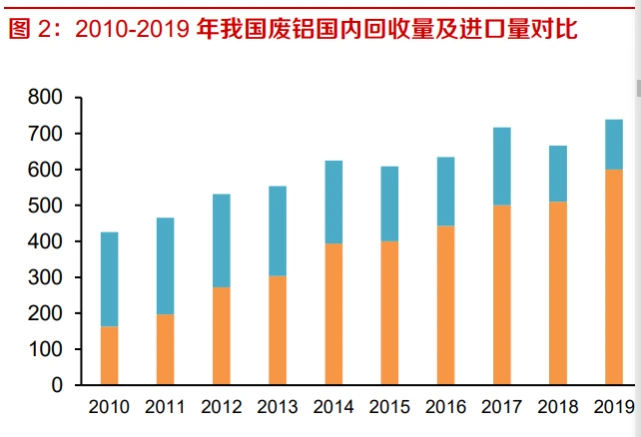
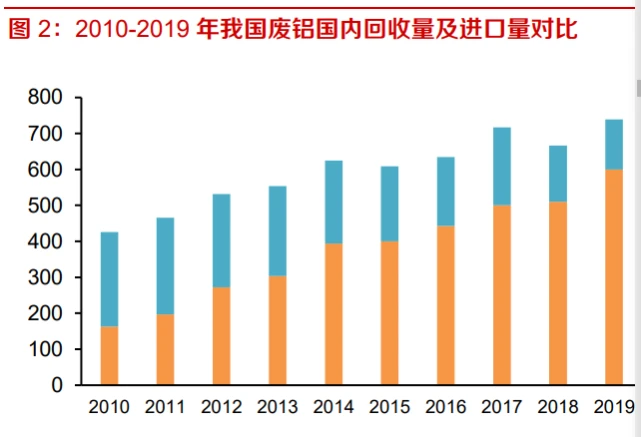
The import volume of scrap aluminum has been declining year by year, and the domestic supply of scrap aluminum needs to be released. From 2011 to 2020, China's production of recycled aluminum increased from 4.4 million tons to 7.35 million tons, with an average annual compound growth rate of 5.3%. The slow growth of scrap aluminum raw material supply is one of the main reasons restricting the development of China's recycled aluminum industry. After 2018, China strengthened the control measures on the import of overseas aluminum scrap, implemented new standards for imported aluminum ingots for trade, and many foreign scrap could not meet the import standards. Superimposed by the impact of the COVID-19 since 2020, the proportion of imported scrap aluminum in the domestic raw materials for renewable aluminum production declined significantly. Due to the declining import volume of scrap aluminum year by year, domestic scrap aluminum has become the main source of raw materials for recycled aluminum in recent years. According to data from the Nonferrous Metals Industry Association, compared to developed countries, China's aluminum industry started relatively late and only took shape in the 1970s. Many aluminum products are still in service, and the domestic supply of scrap aluminum needs to be released.
Transportation, construction, and packaging containers are the main sources of aluminum waste in China. China is a traditional major user of aluminum, and as of the end of 2019, the country's aluminum reserves had reached 340 million tons. According to data from 2018, the transportation sector is the largest source of aluminum scrap recycling in China, accounting for 41%. Next are the construction industry (34%) and packaging containers (21%). The lifespan of aluminum used in construction is 40-60 years, the lifespan of transportation vehicles is 10-20 years, and the lifespan of aluminum used in packaging industries such as food is generally around 1-2 years.
Automobile scrap recycling is dominant, and in the next few years, China will usher in a phase of peak in aluminum scrap recycling. Since entering the 21st century, the annual sales volume of automobiles in China has exceeded 2 million and maintained rapid growth. Considering that the service life of transportation vehicles is 10-20 years, more and more cars will reach their service life in the coming years. According to Mysteel's article "Analysis of Waste Aluminum Import and Supply Forecast", the growth rate of waste aluminum recycling in China's transportation industry from 2021 to 2023 will reach 18% -21%, driving a growth rate of 8% -16% in the total amount of waste aluminum recycling. China will usher in a phase of peak in aluminum scrap recycling.
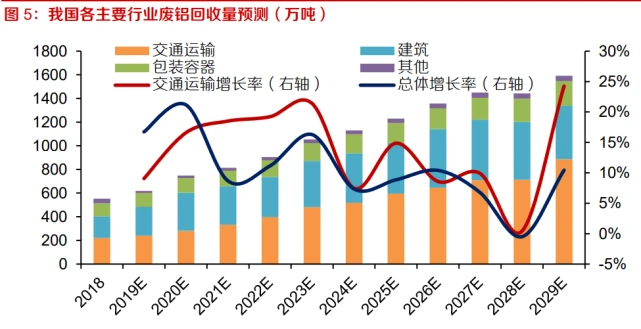
Our country's resource recycling system is also constantly improving, and the production of recycled aluminum will continue to increase. The policies and regulations such as the "Medium - and Long term Plan for the Construction of the Recycling System of Renewable Resources (2015-2020)", the "Promotion Plan for the Development of the Recycling Nonferrous Metals Industry", and the "Development Strategy and Recent Action Plan for the Circular Economy" have made the improvement of the scrap metal recycling system one of the main tasks, stipulating the utilization, standardization, and integration of existing scrap non-ferrous metal recycling channels, accelerating the standardized trading and centralized processing of scrap non-ferrous metals, and gradually forming a recycling and utilization system for scrap non-ferrous metals that covers the whole society nationwide. The improvement of the recycling system for renewable resources has a positive driving effect on the development of the renewable resources industry.
2. Industry trend: China's recycled aluminum utilization level is improving, and cans and automobiles have become key application areas
2.1 China has a high recycling rate for scrap aluminum, but the level of guaranteed recycling and utilization is relatively low
The proportion of scrap aluminum recycling in China has basically reached the level of developed countries. The recycled aluminum industry in China started in the 1970s and has achieved phased results after years of development. By 2019, the overall recycling rate of scrap aluminum in China had reached 76%, making it one of the countries with the highest scrap aluminum recycling rate in the world. According to IAI data, except for cables and aerospace materials with slightly lower recycling rates, the recycling rates of scrap aluminum in other fields have reached the level of developed countries, with the recycling rate of aluminum cans being close to 100%.
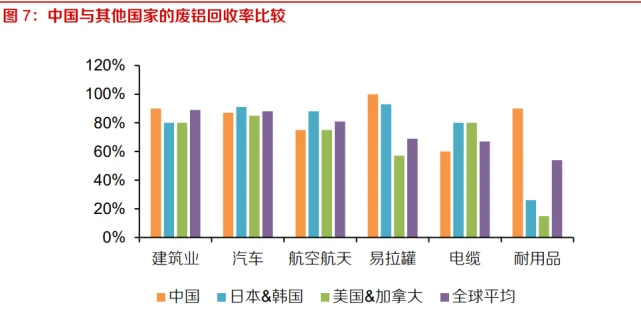
The composition of scrap aluminum is complex, and recycled aluminum is produced in the form of aluminum alloy. Aluminum alloys are widely used in various fields, and the composition of different grades of aluminum alloys varies greatly. After the service life of aluminum alloy products expires, the aluminum content in the waste varies, and it is almost impossible to re refine them into pure aluminum. Even if it can be achieved, the cost is very high and does not have significant economic value. Therefore, after pre-treatment, melting, refining, casting and other production processes, scrap aluminum is produced in the form of alloys (or liquid alloys).
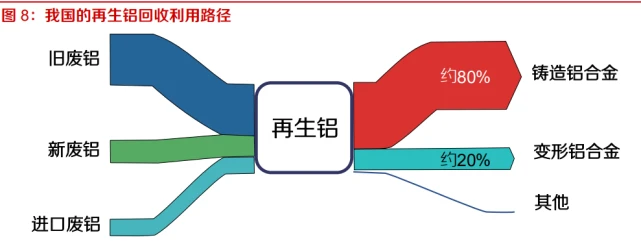
The recycling and utilization methods of scrap aluminum in our country are still relatively backward. For a long time, due to the complex composition of scrap aluminum raw materials, most of the recycled aluminum alloy ingots produced in China have poor ductility and can only be used to produce cast aluminum alloy products. Many high-quality deformed aluminum alloy waste materials are downgraded for use. In this way, the recycling value of aluminum products is greatly discounted, resulting in a huge waste of scrap aluminum resources. According to SMM data, only about 20% of recycled aluminum in China can be re produced into corresponding grades of deformed aluminum alloys each year, achieving grade protection recycling and maintaining the value of waste aluminum. In the structure of recycled aluminum products in developed countries, the proportion of deformed aluminum alloys exceeds half. Therefore, how to do a good job in the graded recycling of aluminum products is an important issue for the transformation, upgrading, and high-quality development of China's recycled aluminum industry.
2.2 Process improvement, the level of recycled aluminum grade protection utilization technology is improving
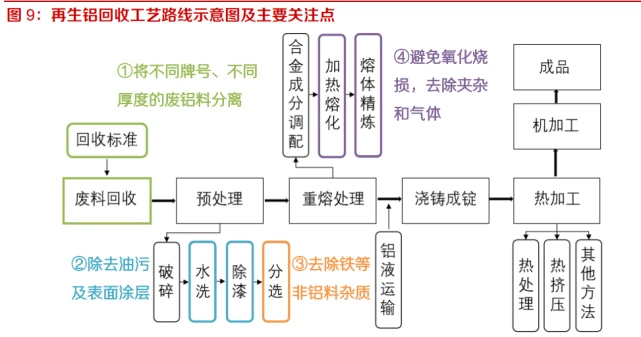
The production of recycled aluminum alloys requires steps such as waste recycling, pretreatment, remelting, casting, and hot processing. At the current stage of industry development, the recycling process of recycled aluminum mainly focuses on the following issues and has made improvements:
Aluminum waste separation. Distinguish between cast aluminum alloy and deformed aluminum alloy and perform rough separation. Separate thin aluminum waste from large pieces of waste aluminum for subsequent melting treatment, reducing the direct erosion and loss caused by high temperature on thin aluminum waste.
Remove oil stains and surface coatings. By using methods such as thermal de coating, chemical de coating, and mechanical de coating, waste aluminum can be cleaned and de coated to reduce harmful gas emissions during the recycling process, improve the water yield of waste aluminum, and enhance the mechanical properties of recycled aluminum alloys.
Remove non aluminum impurities such as iron. Iron is the most common element with excessive content in the smelting of recycled aluminum, which greatly weakens the mechanical properties of recycled aluminum alloys. Remove non-metallic inclusions through methods such as wind selection and flotation; Remove ferromagnetic inclusions through magnetic sorting; Remove other non-ferrous metal inclusions through methods such as heavy media and eddy currents.
Avoid oxidation and burning, remove inclusions and gases. During the smelting process of recycled aluminum, it is prone to react with water vapor in the air, causing oxidation and burning loss, and reducing the yield of recycled aluminum alloy; Impurities will reduce the mechanical properties of recycled aluminum alloys. Adopting a dual chamber furnace production process, material transportation is carried out using sealed conveyor belts to isolate air; Install effective gas collection devices at relevant dust production points. (Report source: Future Think Tank)
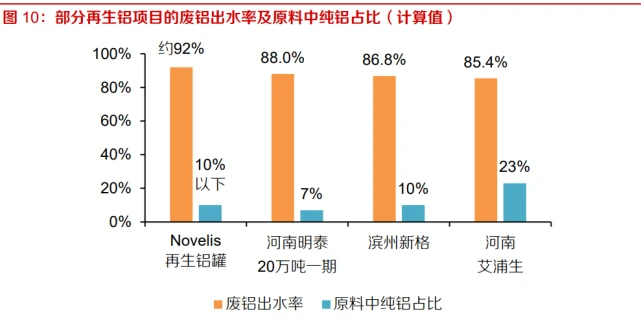
Newly built or put into operation recycled aluminum projects in China have seen an increase in water yield and good profitability. The Henan Aipu Sheng 100000 ton scrap aluminum can preservation and reduction project started construction in 2018 and was put into operation in January 2020. The project has a water output rate of about 85%. Thanks to the improvement of recycled aluminum recycling technology, the effluent rate of newly built or put into operation recycled aluminum utilization projects in China has increased to about 87%. The water yield, which is the proportion of the weight of recycled aluminum in the scrap aluminum raw material, is an important indicator for the operation of recycled aluminum enterprises. Although there is still a gap from the world-class level, it represents a considerable level of profitability.
In the raw material ratio of newly built or newly put into operation recycled aluminum projects in China, the proportion of pure aluminum has reached the international level. If recycled scrap aluminum is used entirely as raw material, the alloy composition produced by smelting usually cannot meet the actual production process requirements. Therefore, it is necessary to add some pure aluminum to adjust the chemical composition, so that its chemical composition meets the requirements for grade protection and utilization. The proportion of pure aluminum added to the recycled aluminum cans of Novelis, an international leader in recycled aluminum, has been reduced to less than 10%. The proportion of pure aluminum in the raw materials of Henan Mingtai's annual processing of 200000 tons of scrap aluminum project (Phase I) is as low as 7%, and the proportion of pure aluminum in the raw materials of other domestic recycled aluminum projects has also decreased significantly. The overall technical level of recycled aluminum projects is improving.
In the future, aluminum cans and automotive aluminum materials will be key areas for the development of scrap aluminum recycling and reuse. The main sources of aluminum scrap recycling in China come from transportation, construction industry, and packaging containers. The aluminum alloy composition in the construction industry is relatively broad and easy to recycle. Currently, the recycling of 6-series aluminum profiles is the most common in the domestic market. In addition, high-grade aluminum materials such as aluminum cans can be downgraded and recycled into cast aluminum alloys for the production of aluminum alloy doors and windows. Aluminum alloys used for cans and cars require high performance indicators, are difficult to produce, and have high recycling value. Therefore, in the future, aluminum cans and automotive aluminum materials will be the key areas for the development of scrap aluminum recycling and reuse.
3. Aluminum cans: catching up with the advanced level of international grade protection and recycling
3.1 The economic benefits of grade protection recycling of aluminum cans are significant
All aluminum cans are made of three types of aluminum alloys, and simple mixing can only be used in a downgraded manner, resulting in waste. Aluminum cans are the most common aluminum products in our daily lives and also the most mature aluminum products in the current recycling system. All aluminum cans are usually made of three types of aluminum alloys. The can body and bottom are connected as a whole with 3104 alloy, the can lid is made of 5182 alloy, and the pull ring is made of 5052 alloy. If backward technology is used to simply mix the cans as a whole, all of these aluminum materials will be downgraded and used to produce low value-added cast aluminum alloys such as sub brand 102 and ADC-12, which will cause significant economic waste.
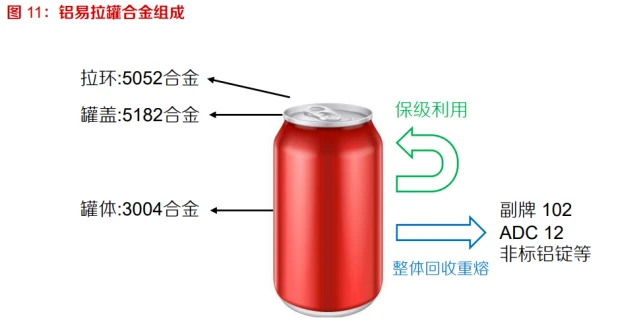
Guaranteed recycling and reuse, achieving the recycling from "old cans" to "new cans". By adopting the method of guaranteed recycling, the tank body and lid are first separated by specialized pretreatment equipment, and then subjected to professional crushing, paint stripping, and delamination treatment, the tank body and lid can be respectively made into corresponding recycled 3104 aluminum alloy and recycled 5182 aluminum alloy. Produce new aluminum cans from recycled aluminum alloy, ultimately achieving the recycling process from "can" to "can".
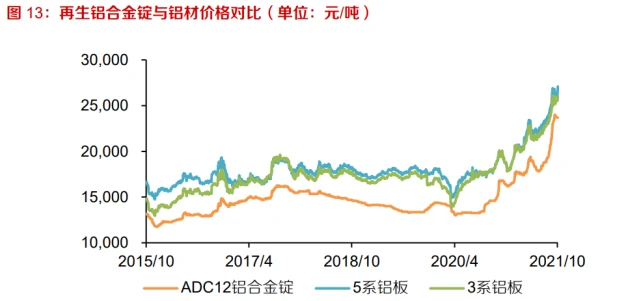
Guaranteed recycling maximizes the economic benefits of aluminum cans. The prices of recycled 3104 aluminum alloy and recycled 5182 aluminum alloy are determined based on the market price of the corresponding primary aluminum alloy, while ADC-12 and other cast aluminum alloys are usually priced by the buyer, and the guaranteed recycling significantly maintains the economic benefits of aluminum cans. If the added value of manufacturing recycled aluminum cans is added, the maximum value of aluminum cans can can be maximized through grade protection recycling.
3.2 Catch up with the international advanced level of aluminum can grade protection recycling and utilization
The international recycling and reuse of aluminum cans has become relatively mature. In recent years, all aluminum plate and strip production enterprises in developed countries in Europe and America that commercially produce aluminum can materials have established waste can recycling and regeneration projects. The largest project has a production capacity of 400000 tons/year for regenerating 3104 alloy flat ingots. The content of waste cans in aluminum cans produced globally is increasing, with an average waste can content of 60% for 3104 aluminum alloy in countries and regions other than China in 2020. Novelis Aluminum Company (Novelis) is the world's largest producer of 3104 alloy foil, cans, and strips, accounting for almost 45% of global production, with a waste can content of up to 90%, truly achieving optimal recycling.
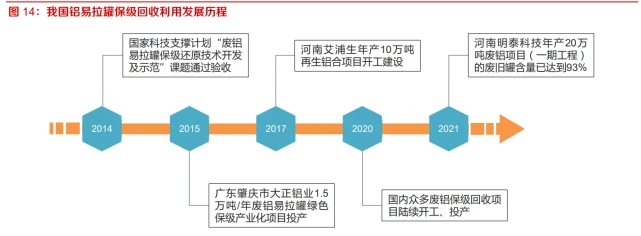
China's aluminum can recycling started late and has developed rapidly in recent years, with leading enterprises taking the lead in reaching the international advanced level. The "12th Five Year Plan" National Science and Technology Support Program project "Development and Demonstration of Waste Aluminum Can Maintenance Reduction Technology" in 2014 has passed the acceptance inspection. Guangdong Zhaoqing Dazheng Aluminum Industry has implemented the transformation of scientific and technological achievements, and the 15000 ton/year waste aluminum can green maintenance industrialization project was put into operation in 2015, opening the way for China's waste aluminum can maintenance utilization. Until 2019, only the Henan Aipu Sheng project with an annual output of 100000 tons of recycled aluminum alloy was put into operation. Since 2020, numerous domestic projects for the use of 3004/3104 aluminum alloy for cans have started construction and production. Among them, Henan Mingtai Technology Development Co., Ltd.'s annual processing of 200000 tons of waste aluminum project (Phase I) has achieved a waste can content of 93%, which has reached the international advanced level and has obvious technological advantages.
4. Aluminum for automobiles: The goal of "decarbonization of materials" drives the development of automobile manufacturing towards "closed-loop recycling"
4.1 Cooperation between Recycled Aluminum Enterprises and Automobile Companies to Establish a "Closed loop Recycling" of Recycled Aluminum
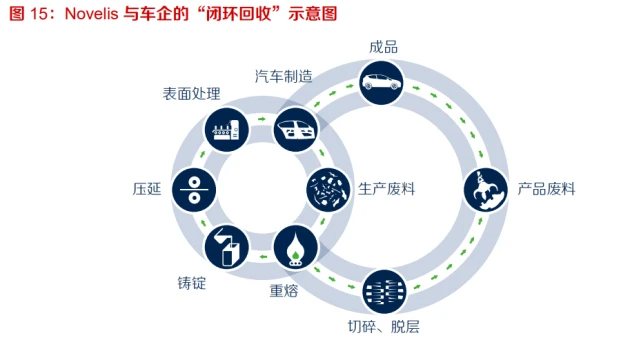
Recycled aluminum enterprises and automobile companies establish a "closed-loop recycling" system, significantly improving the recycling and utilization rate of metal materials. Closed Loop Recycling refers to the production of corresponding grades of deformed aluminum alloys from waste materials generated by downstream enterprises or recycled aluminum after consumption, which are then supplied to downstream enterprises or end consumers. It is a more advanced level of graded recycling mode. Developed countries abroad attach great importance to the graded recycling of scrap aluminum, and excellent enterprises maximize the resource value of scrap aluminum by carrying out closed-loop recycling cooperation with downstream enterprises for deformed aluminum alloys. Taking international recycled aluminum giant Novelis as an example, Novelis has collaborated with major automakers such as Ford and Volvo to establish a closed-loop recycling system for "automotive panels stamping waste automotive panels". By producing automotive panels from stamping waste and recycled scrap automotive panels, Novelis can significantly reduce the demand for primary aluminum and the addition of alloying elements to customers. By establishing a closed-loop recycling system, Novelis is able to recycle and reuse 90% of the metal waste from Ford pickup truck bodies.
4.2 Recycled aluminum plays an important role in the "full process carbon reduction" of automobiles
The raw material acquisition stage is included in the scope of carbon emissions accounting for the lifecycle of passenger cars. The latest "Technical Specification for Life Cycle Carbon Emission Accounting of Passenger Cars" proposes to include the stages of raw material acquisition, vehicle production, and use in the scope of life cycle carbon emission accounting for passenger cars. The raw material acquisition stage, which includes the acquisition of resources and the production of materials, includes processes such as resource extraction, processing, and manufacturing at the system boundary.
When green energy becomes the dominant energy source, material production will become a key focus of carbon reduction. In the context of "carbon neutrality", the automotive industry is gradually transitioning from gasoline vehicles to pure electric vehicles, and the carbon emissions of passenger cars during the usage phase have been significantly reduced. The proportion of carbon emissions from automotive raw materials has significantly increased in pure electric vehicles, so the stage of obtaining high energy consuming and high emission automotive raw materials will become a key focus of future carbon reduction.
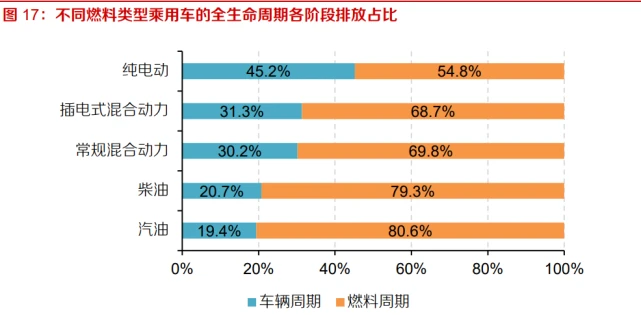
Major multinational car companies have successively announced their "carbon reduction schedules" and put "full process carbon reduction" on the agenda. In the context of global carbon neutrality, decarbonization and emission reduction have become the focus of attention in the automotive industry. As of now, major multinational cars including Daimler, Volkswagen, BMW, Volvo, and Nissan have successively announced their respective "carbon reduction" targets. Taking Volvo as an example, it plans to use more recycled and bio based materials in its products by 2025 to minimize the carbon dioxide emissions of the materials. This includes 25% recycled plastic, 25% recycled steel, and 40% recycled aluminum, as well as batteries containing recycled components.
Domestic car companies may strengthen cooperation with recycled aluminum enterprises, and recycled aluminum leaders are expected to build barriers. China occupies an important position in the global new energy vehicle market. Although only Great Wall Motors has publicly announced that it will achieve "carbon neutrality" by 2045, it is expected that domestic car companies may follow the trend of "material carbon reduction". Automobile companies may deepen their cooperation with recycled aluminum enterprises and achieve stricter carbon reduction goals by establishing a "closed-loop recycling" system. (Report source: Future Think Tank)
4.3 Recycled Aluminum Faucet: From Passive Recycling to Active Launch of Aluminum Solution
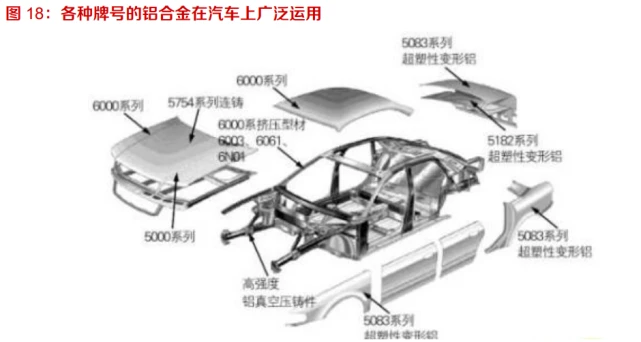
The aluminum alloy sheet used in automobiles is complex, and the difficulty of grade protection and recycling increases. Aluminum alloy materials are widely used in automobiles, and different series and models of plates, profiles, pipes, and high-performance cast aluminum materials are used for different stress bearing parts. The skeleton part bears the greatest force and is made of 2000 series or 7000 series materials with the highest copper content and high hardness. The secondary load-bearing parts such as exterior panels, doors, and floors are made of 5000 series materials mainly containing magnesium elements and 6000 series materials with high magnesium silicon content and good corrosion and oxidation resistance. This undoubtedly increases the difficulty of maintaining and recycling automotive scrap aluminum.
Recycled aluminum faucets are involved in the design of automotive aluminum materials, and by collaborating with car manufacturers to improve the recycling efficiency of recycled aluminum, they occupy a favorable position in the industry. In order to further improve the level of maintenance and recycling of automotive aluminum materials, Novelis has proactively launched aluminum solutions and collaborated with customers to develop 6xxx automotive interior panels. This advanced alloy development concept breaks away from the existing alloy combination of 6xxx automotive exterior panels and 5xxx automotive interior panels, effectively reducing the types of automotive panel alloys, improving their recycling efficiency, and reducing recycling costs. In this process, Novelis greatly enhanced its cooperation stickiness with car companies and occupied a favorable position in the industry due to its technological advantages and deep cooperation with car companies.
(This article is for reference only and does not represent any investment advice from us. If you need to use relevant information, please refer to the original report.)
Selected report source: Future Think Tank.